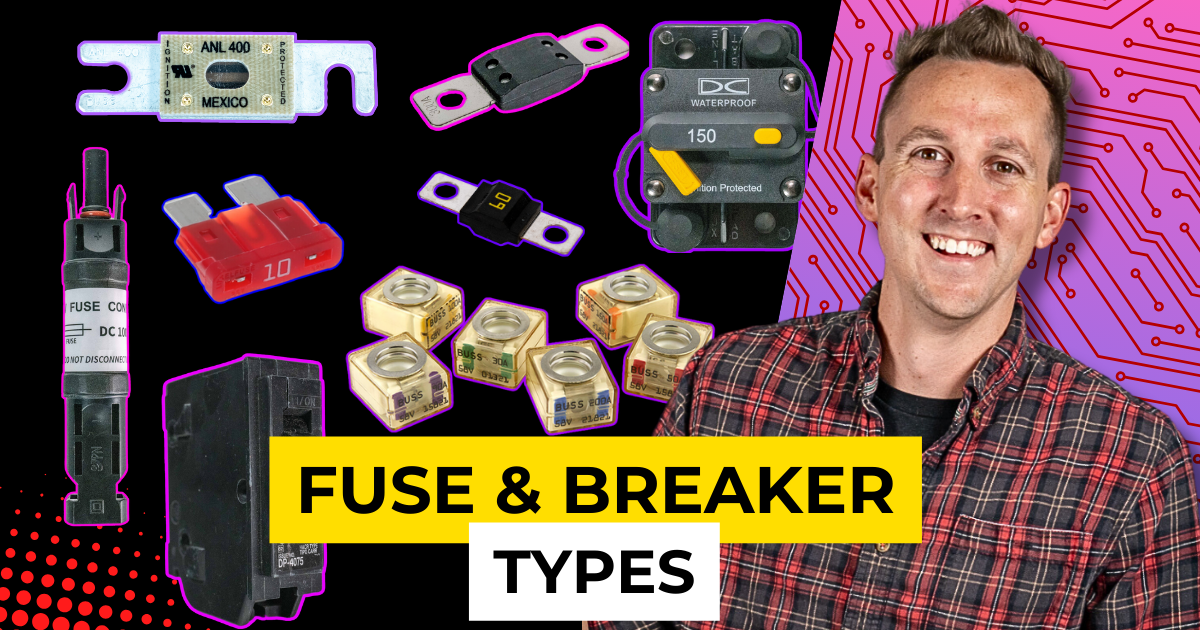
Not all fuses and breakers are created equal, and selecting the right type is essential for maintaining your electrical system’s safety. In this second lesson of the Breakers, Fuses, and Overcurrent Protection chapter, we’ll explore the various types of fuses and circuit breakers, their functions, and where they’re used.

Fuses and Breaker Types 101 – Video:
AC Circuit Breakers

AC breakers are a familiar sight in residential breaker boxes, and they play a crucial role in protecting 120V AC circuits.
- Design: Power enters through the back slot and exits via a screw terminal. The breaker mechanism connects and disconnects the circuit as needed, either for maintenance or during an overcurrent event.
- Types:
These are ideal for AC circuits in mobile and off-grid systems, as detailed in EXPLORIST.life wiring diagrams.
DC Circuit Breakers

DC breakers function similarly to their AC counterparts but are designed for direct current.
- Operation: Power flows in through one terminal and out the other. A manual button or internal mechanism disconnects the circuit during maintenance or an overcurrent event.
- Use Cases: Commonly used to protect DC circuits in systems with components like solar charge controllers and DC-to-DC chargers.
DC Fuses
DC fuses are a critical component of electrical systems, offering permanent overcurrent protection. Let’s explore the different types:

ANL Fuse
- Features: High-amperage capacity, ideal for main system protection.
- Application: Used as the main system fuse in wiring diagrams at EXPLORIST.life.
- Operation: A filament inside melts to break the circuit during an overcurrent event.
Mega Fuse
- Features: Similar to the ANL fuse but without a visible filament window.
- Application: Protects large component circuits like inverter/chargers and solar charge controllers.
MIDI Fuse
- Features: A smaller version of the Mega fuse.
- Application: Often used in Sprinter vans for DC-to-DC chargers or in compact fuse holders like the Blue Sea SafetyHub.
Blade Fuse
- Features: Commonly found in vehicles, with amperage ratings from 1A to 30A.
- Application: Protects smaller circuits in cars and off-grid systems.
MRBF Fuse
- Features: Compact and mounted directly to battery terminals via an MRBF fuse holder.
- Application: Protects wires from starter batteries to DC-to-DC chargers, especially in alternator charging setups.
PV Fuse
- Features: Designed for solar arrays, with waterproof and weather-resistant housings.
- Application: Protects solar panels in outdoor installations.
Choosing the Right Protection
Selecting the right fuse or breaker depends on your system’s design and components. Each fuse or breaker type serves a specific purpose, whether protecting high-amperage circuits, compact systems, or solar installations.
- Key Considerations:
- Ensure the fuse or breaker matches your system’s voltage and current requirements.
- Refer to wiring diagrams, such as those available at EXPLORIST.life, for precise recommendations.
What’s Next?
Now that you understand the different types of fuses and breakers, it’s time to learn where to install them in your system. Watch the next lesson in this playlist to master fuse placement and ensure optimal safety and functionality in your off-grid electrical setup.