When building an electrical system for a camper, boat, or off-grid setup, selecting the right fuse or breaker size is a critical step. Too large of a fuse? Your system might go unprotected and face fire risks. Too small? You’re in for constant headaches with blown fuses. In this lesson, part of the Breakers, Fuses, and Overcurrent Protection playlist, we’re diving deep into how to properly size fuses and breakers to keep your system safe and efficient.

Why Fuse Sizing Matters
Fuses and breakers act as the safety net for your electrical system. They protect your wiring from carrying more current than it’s designed for, which could lead to overheating or fire. But here’s the thing: manufacturers of components like chargers or controllers often recommend fuse sizes. In many cases, it’s easiest and safest to follow their guidance—unless the specified fuse size doesn’t exist.
For example, I recently came across a charge controller recommending a 33A fuse. A 33A fuse isn’t readily available, so understanding the math behind fuse sizing lets us adapt and find safe, practical alternatives.
The Basics of Fuse Sizing
To correctly size a fuse, we need to determine two key values:
- Minimum Fuse Size
This value is the amperage rating of the connected device. For example, a 100A charge controller needs at least a 100A fuse. - Maximum Fuse Size
The American Boat and Yacht Council (ABYC) specifies that the maximum fuse size can be up to 150% of the wire’s ampacity.For instance, a 2AWG wire with 105°C insulation has a maximum ampacity of 210A. Multiplying that by 1.5 gives us a maximum fuse size of 315A.
Real-World Application
Let’s apply these principles to a simple example:
- Wire: 2AWG
- Device Load: 100A
We know the minimum fuse size is 100A. The maximum, based on ABYC guidelines, is 315A. But to ensure efficiency and minimize tripping, we recommend a fuse size closer to 120% of the load rating—in this case, 120A. If 120A fuses aren’t available, rounding up to 125A or 150A is acceptable, as both fall within the safe range.

Sizing Fuses for Distribution Systems
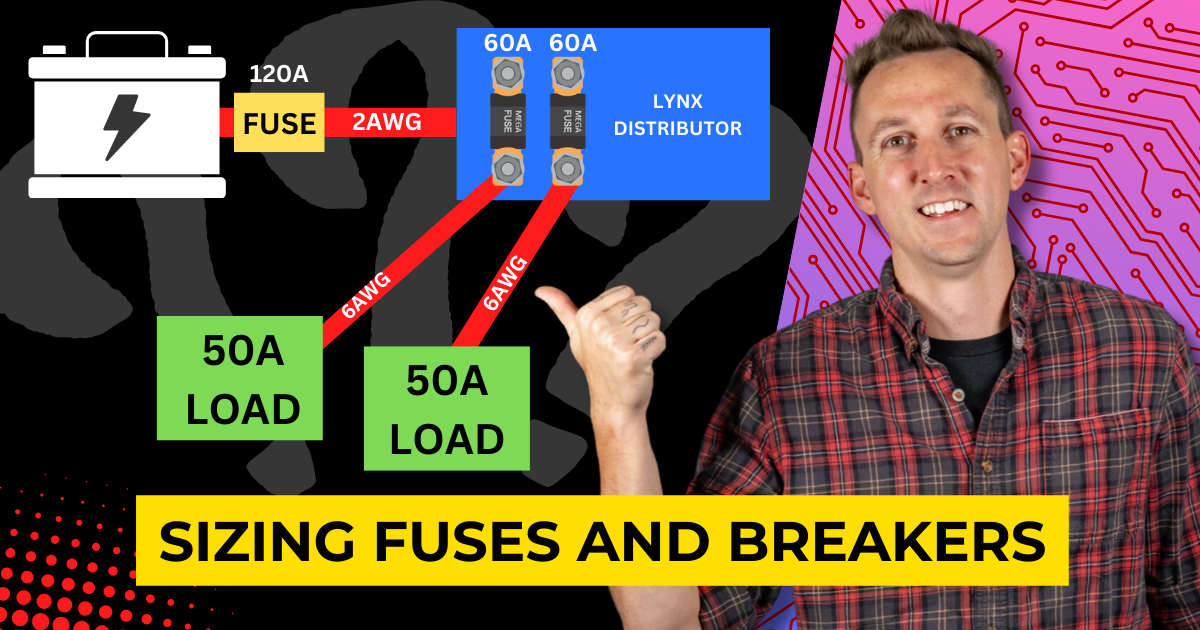
If you’re using a distribution hub like the Lynx Distributor or Blue Sea SafetyHub, each wire segment needs its own calculation. For example:
- A 50A charger connected with 6AWG wire (ampacity: 120A) allows a fuse size between 50A and 180A.
- Using the 120% rule, a 60A fuse is recommended.
If the fuse you need isn’t available, round up to the next size, ensuring it stays within the safe range.

A Note on AC Circuits
AC circuits are simpler to size. Breaker sizes correspond directly to the wire size:
This approach covers most camper vans, boats, and off-grid systems.
Simplifying Fuse Sizing with Kits
If all this math feels overwhelming, you’re not alone. That’s why every kit in the EXPLORIST.life shop comes pre-equipped with correctly sized fuses and breakers. Still, understanding the process is valuable—education is power, after all!